Additional System Startup & Scheduling Methods
Crontab
- Popular Unix tool for executing scheduled tasks
- OS X still allows the use of cron for scheduling
- Not frequently abused due to the ease of visibility into the cronjob
- If you go to edit your cronjob, you will see the malicious one as well
- crontab -e allows you to edit your scheduled tasks
- crontab -l prints scheduled tasks
- Files stored in plaintext
- Stored in /usr/lib/cron/tabs
- Cron is enabled by default on OS X
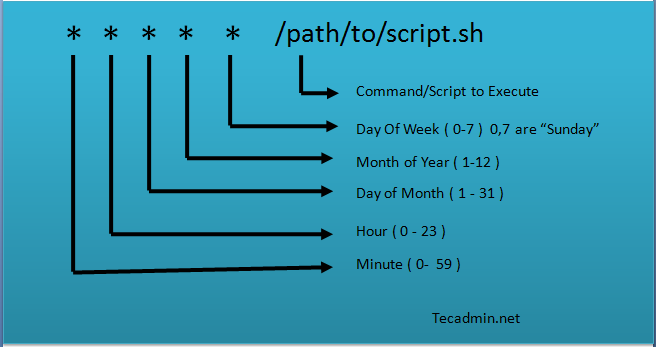
- Some built in features include:
- @reboot /path/to/script -> Will run script at every system startup
- @yearly /path/to/script -> Will run script at the first minute of every year
- @monthly /path/to/script -> Will run script 00:00 on the 1st of every month
- @daily /path/to/script -> Will run a daily log file cleanup using the cleanup-logs shell script at 00:00 each day
- When collecting cron data, ensure you are dumping the user and root user crontab
Persistence via KEXT
- Kernal Extension file
- Allow the kernel to communicate with hardware
- /System/Library/Extensions
- KEXT files built into the OS X operating system
- /Library/Extensions
- Advanced malware may not even bother to use a launch daemon or agent if they have root access
- Would instead maybe use a KEXT file
- Attackers can build a KEXT in advanced and move to the victim system
- Attackers can also use a KEXT file and launch daemon or agent for a backdoor
- Keyloggers can be set up via a KEXT module
- C2 server is communicated with via a launch daemon
- Keep an eye out for KEXT files that do not exist in those directories
- Starting in Yosemite, you can no longer place unsigned KEXT files in either startup location
- KEXT files are bundles or folders that Finder will treat as one file
- KEXT bundles can contain the following:
- Information property list (info.plist)
- Holds settings and requirements related to KEXT
- KEXT binary
- Binary that the KEXT will be responsible for executing
- Mach-O format
- Resources
- Icons or other items that might be packaged with the driver if it needs to display a menu
- KEXT bundles
- Allows for plugins or other KEXTs that it is dependent on
KEXT Commands
- List currently loaded KEXT files with the kextstat command

- Loaded or unloaded via kextunload and kextload
- Ex. sudo kextunload /path/to/file
- Can also use the CFBundle name
- Ex. sudo kextload /path/to/file
- codesign can be ran on KEXT bundles
- Will tell you what KEXTs are signed and who signed them
Less Popular Persistence Mechanisms
- launchd was not introduced until OS X 10.4 (Tiger)
- Not always responsible for ensuring everything boots up correctly.
- Some old persistence mechanisms have been deprecated in favor of launchd
- com.apple.loginitems.plist
- Property list used to run services when a user logs in
- Located in /Users/$USER/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginitems.plist
- Contains a list of apps to run at start up
- More service like such as Dropbox or Google Drive
- View these by running ‘defaults’ or ‘plist-buddy’ on the plist.
- ‘at’ command
- Apple has disabled the usage of at as a scheduler by default, but it still comes installed on the OS
- ‘at tasks’ are used to schedule tasks at a specific time
- Not like cron due to being one time tasks that are removed after execution
- Can survive a system restart
- Enable the tasks using launchctl
- sudo launchctl load -F /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.atrun.plist
- Will print a hello world to /tmp/hello.txt
- View a user’s at tasks with ‘atq’
- Collect verbose at tasks from /private/var/at/jobs
- Even if a task is not executed, it will still be in here
- Will be stored with a random identification number
- Ex. /private/var/at/jobs/a000080170e832
- Printing the file will show user information and variables followed by the command the user has scheduled
- init
- Before launchd, init was used and functions differently
- Back when it was responsible for system startup, plists were not used
- Would run rc scripts
- Bash scripts with some variables and a path to a target process
- Executing from /etc/rc.common does not work on El Capitan
- launchd.conf
- Deprecated as of Yosemite
- launchd used to refer to config files to collect custom settings
- Only existed if manually created
- Found at /etc/launchd.conf
- launchctl bsexec
- Tells the launchd to execute a specific process

